SAP GRC customers often find themselves in functional and organizational silos—specifically between Security and ICS—missing out on efficiency and synergy-related opportunities. We aim to help overcome these silos by following a more integrated approach and demonstrating how to leverage the integration capabilities between SAP Process Control and SAP Access Control. Below, we abstract the Content and Process views and summarize the related capabilities.
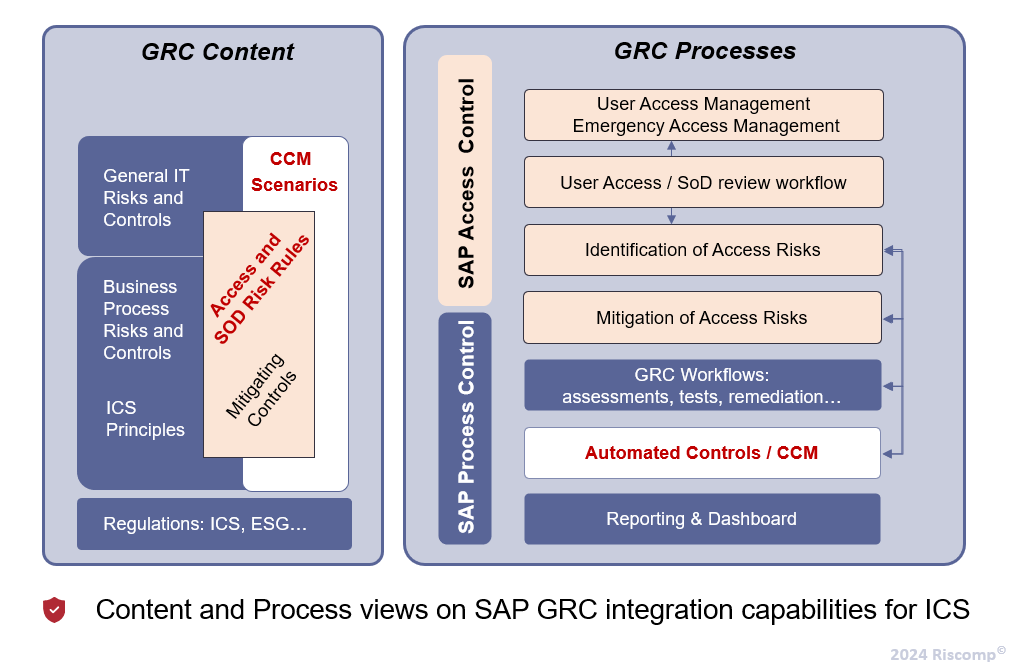
Content View:
- Framework Capabilities: Designed to document all risk and control layers, considering COSO, COBIT, and other methodologies. This includes IT and business processes, as well as entity-level controls often referred to as ICS principles.
- Operational and Strategic Risks: Managed in SAP Risk Management, these can be part of the ICS framework if a harmonized data model is adopted in SAP GRC.
- Multiple Compliance Frameworks: Manage several initiatives in parallel, either separately or closely intertwined. For example, ESG, NIS2/Cybersecurity, and other regulations can be added on top of a core ICS regulation. SAP GRC comes with pre-configured SOX and FDA regulations. Regulations can be further broken down into requirements, such as reflecting a more detailed structure for GDPR on the level of individual paragraphs.
- Flowcharting: It is essential to be able to link risks and controls with business processes, and integration with SAP Signavio is the way to go. Customers and consultants are encouraged to collaborate with SAP to enhance it further. We highly recommend participating in the upcoming GRC Improvement initiative: SAP Influence Campaign. We will dedicate one of our next posts to this.
- Automation Aspects: Controls involved in ICS activities can be automated:
- Access Control: Leveraging Access Risk Analysis (ARA) functionality. It can be extended with SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance (IAG).
- Process Control: Leveraging the CCM framework in SAP GRC.
- Important: Mitigating controls used in SAP Access Control can be part of the overall ICS framework.
Process View:
- Provisioning and FireFighting: Access Request Management (ARM) functionality, with integrated risk analysis and a flexible approval process, along with Emergency Access Management (EAM or FireFighter) functionality, are crucial controls that significantly reduce risks in identity access management and authorization domains.
- User Access and SoD Review Workflows: These add value by establishing recurring workflow-based control activities over user access.
- Important: Access Risk Analysis can be linked with controls in SAP Process Control via the CCM framework by using the scenario type “SoD” when creating data sources. This approach helps achieve the following:
- Incorporating SoD controls into the overall ICS framework.
- Extending report-based access risk analysis, making it more binding by introducing role-based accountability.
- Workflows: Automated monitoring results delivered by the CCM framework can be embedded into ICS activities in several ways, including monitoring workflows, standalone usage of business rules, direct integration with manual control performance workflows, and more.
If you’re eager to learn more, feel free to reach out to us! Stay tuned and sign up for our newsletter.
